Understanding the injection molding process can seem daunting at first. However, with the right insights, it becomes manageable. Renowned expert Dr. Emily Carter states, "Grasping the injection molding process requires patience and practice." This highlights the complexity of the industry.
The injection molding process involves several crucial steps. Materials are heated and injected into molds, where they cool and solidify. This creates a wide range of products, from small components to large parts. But the details matter; even minor adjustments can lead to defects.
Many beginners overlook the importance of temperature control and cycle times. These factors are vital for quality. Errors can occur without proper monitoring. Understanding these nuances makes a significant difference. The injection molding process is both an art and a science, encouraging continuous learning and improvement.
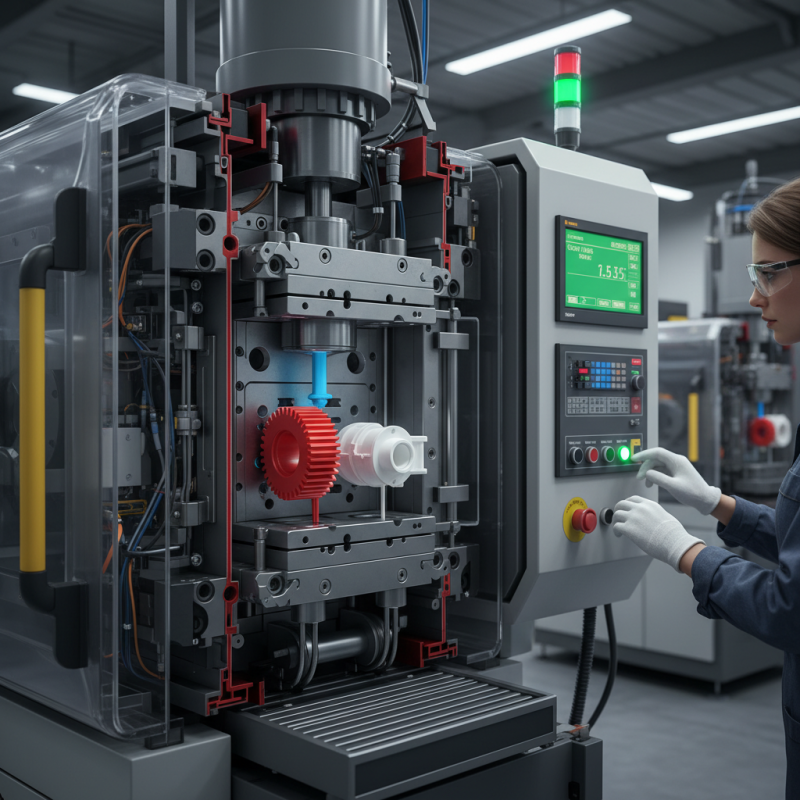

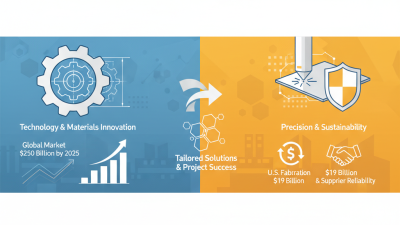
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts by injecting material into a mold. This method is integral to various sectors, including automotive, medical, and consumer goods. According to industry reports, the global injection molding market size was valued at over USD 220 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow significantly. This growth illustrates its critical role in production efficiency and material optimization.
One of the biggest advantages of injection molding is its ability to create complex shapes with high precision. Molds are often made of steel or aluminum, influencing durability and cost. However, designing a mold can be expensive upfront. It may take time to ensure that the mold functions perfectly. Mistakes in design can lead to wasted materials and higher production costs.
Tips: When venturing into injection molding, pay close attention to the design phase. Prototyping can catch issues early. Always consider the materials that you will use. Some plastics recycle better than others.
Injection molding is also favored due to its scalability. Once the initial costs are covered, the long-term production can be very efficient. Yet, production runs must be carefully planned. Rapid changes in design can lead to costly adjustments. Balancing elasticity in design with cost-effectiveness is necessary for operational success.
| Dimension | Description | Examples of Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Material Types | Common materials used in injection molding including thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers. | Containers, automotive parts, plastic toys. |
| Process Steps | Includes material feeding, heating, injection, cooling, and ejection. | Production of complex shapes and designs across various industries. |
| Cycle Time | The time it takes to produce a single part or a batch of parts; typically ranges from a few seconds to several minutes. | High-volume production runs, such as consumer electronics and household goods. |
| Advantages | Allows for high precision, repeatability, and lower production costs in large quantities. | Medical devices, appliance parts, and intricate components in engineering. |
| Challenges | Initial setup costs, mold design complexity, and material limitations can be challenging. | Custom molds for unique designs, time investment in design phase, and managing scrap rate. |

The injection molding process involves several key components that are crucial for creating high-quality products. The main elements include the injection molding machine, molds, and plastic material. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global injection molding market is expected to reach $313.5 billion by 2027, highlighting its growing importance in manufacturing.
The injection molding machine operates by melting plastic pellets and injecting them into a mold. This mold is designed to shape the final product. Proper temperature control during melting is essential. If the temperature is too high or too low, defects like warping can occur. Molds can be complex, often containing multiple cavities. This complexity can lead to higher costs and longer lead times. Balancing mold design and production efficiency remains a challenge for many manufacturers.
Plastic materials are another vital component. There are various types of plastics used, each with unique properties. For instance, polyethylene is popular for its flexibility, while polycarbonate is chosen for its strength. However, selecting the right plastic is tricky. Incorrect choices can lead to severe quality issues. Understanding the interaction between materials and the final application is crucial for successful injection molding.
Injection molding is a complex process. It is widely used for mass production. Understanding it step-by-step makes it easier. Each phase plays a critical role in creating parts.
The initial step involves designing the mold. This design must be precise. A tiny error can lead to defects. Next, the mold is built. Fabrication requires skilled workers. After that, raw plastic is heated until it melts. This liquid plastic is injected into the mold. The pressure applied is significant. It ensures every detail of the mold is filled.
Cooling follows the injection phase. It takes time for the plastic to harden. Sometimes, this step is rushed, leading to weak parts. Once cooled, the mold is opened. The finished parts are ejected. Quality checks occur at this point. Imperfections can still appear. Many factors influence the success of the injection molding. It's important to notice and learn from these challenges.
Injection molding is a popular manufacturing process. It allows for the production of various objects using different materials. Understanding these materials is crucial for beginners in the field.
Plastics are the most common materials used in injection molding. Polypropylene is lightweight and resistant to chemicals. It is often used for packaging and automotive parts. Another frequently used plastic is ABS. This material is known for its strength and impact resistance. It is commonly found in toys and electronic housings.
Beyond plastics, metals like aluminum are gaining traction in the injection molding process. They offer superior strength and thermal conductivity. However, working with metal requires more advanced techniques. There are challenges here, such as potential warping during cooling. Beginners must consider these factors carefully. Knowledge of material properties can lead to better product quality.
Troubleshooting in injection molding is essential for achieving high-quality products. According to industry data, approximately 30% of production issues stem from improper machine settings. This can lead to defects like short shots or uneven finishes. For beginners, understanding these basics is crucial.
Common issues often arise during the cooling phase. If the cooling time is insufficient, parts can warp. A study revealed that 70% of defects are temperature-related. It's important to monitor mold temperatures closely. A temperature variance of even a few degrees can alter dimensions.
Additionally, material selection plays a significant role. Not every polymer works well for all applications. Inconsistent materials can cause bubbling or weak spots. Inspecting the material quality is vital before starting production. Reflections on these issues can lead to better processes and improved final products. Embracing imperfections helps in refining techniques and achieving manufacturing excellence.




You are using an outdated browser. Things may not appear as intended. We recommend updating your browser to the latest version.
Close