Plastic molding is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. It transforms raw plastic into finished products. This technique supports a variety of industries, from automotive to consumer goods. According to a recent report by Market Research Future, the global plastic molding market is projected to reach $650 billion by 2025.
The diverse types of plastic molding techniques meet different application needs. They include injection molding, blow molding, and rotational molding. Each technique has its unique advantages and challenges. For instance, injection molding is highly efficient for mass production. However, it requires high startup costs and can create waste if not managed properly.
Understanding these techniques is essential for any manufacturing professional. Innovators must weigh costs against production quality. This balance can be tricky. Often, companies prioritize speed over accuracy, leading to defects. Exploring the best methods in plastic molding allows businesses to improve their processes and products.

Plastic molding techniques play a critical role in manufacturing. Each technique offers distinct advantages and is suitable for specific applications. Understanding these methods can help in choosing the right one for your project.
Injection molding is one of the most common methods. It involves injecting molten plastic into a mold. This technique is efficient for mass production. However, it requires a high initial investment. The complexity of the mold can lead to delays and increased costs.
Blow molding is ideal for creating hollow objects, like bottles. This method requires less material than injection molding. Still, it has limitations in terms of design complexity. Some shapes are challenging to achieve. Rotational molding, on the other hand, is great for larger items. It provides uniform wall thickness but has slower production speeds.
Compression molding is another option. It’s often used for rubber and thermoset plastics. This process can lead to waste if not managed carefully. Each technique has its pros and cons, making careful consideration essential.
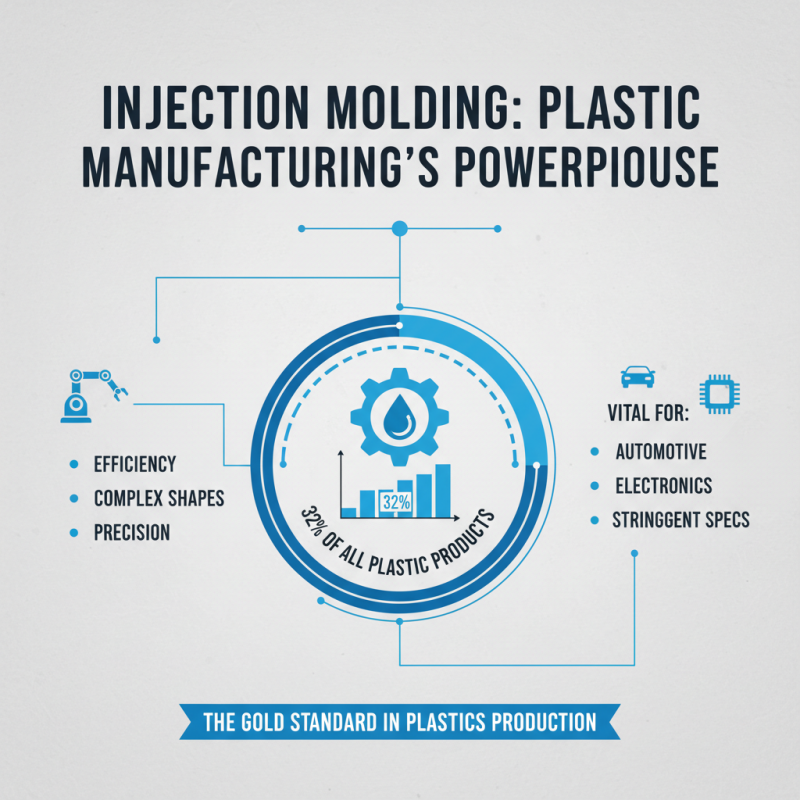
Injection molding stands out as one of the most efficient processes in plastic manufacturing. According to industry reports, around 32% of all plastic products are made using this technique. Its ability to create complex shapes while maintaining precision is unmatched. This is vital for industries like automotive and electronics, where specifications are strict.
However, challenges exist. Mold design can be costly upfront, often requiring extensive testing. This initial investment can deter smaller producers. Furthermore, material waste is an issue. Reports indicate that around 5% of raw materials can be lost during the injection process. Balancing efficiency and sustainability remains a hot topic.
Still, injection molding’s advantages largely outweigh its drawbacks. Production rates can reach 60 parts per minute, making it ideal for mass production. This method fulfills the demand for high-volume products efficiently. Companies must keep refining their processes to reduce waste and improve quality control. Embracing innovation can lead to better outcomes in the long run.
Blow molding is a key technique in the plastic manufacturing industry. This method creates hollow plastic products efficiently. It utilizes a process where air inflates soft plastic into a mold. The outcome is often lightweight, durable items such as bottles and containers.
One of the main benefits of blow molding is its versatility. It can produce varying shapes and sizes. However, not every design is suitable. Intricate shapes may be challenging to achieve. Sometimes flaws appear during production. Those issues require careful planning and adjustments.
Blow molding's efficiency is notable, yet, it isn't perfect. The equipment can be costly, impacting smaller businesses. There’s also the risk of waste material. Careful management is needed to minimize excess. In the end, while blow molding is excellent for many applications, it demands a thoughtful approach.
Rotational molding stands out as a go-to method for producing large, hollow plastic parts. This technique involves heating a mold filled with powdered resin. The mold then rotates around two axes, ensuring an even distribution of the material. This process is particularly beneficial for creating items like tanks, toys, and playground equipment. According to industry reports, rotational molding can produce parts up to 10 feet in diameter, which is often unmatched by other techniques.
One advantage of rotational molding is its versatility. It allows for complex shapes, and it can accommodate a variety of materials. However, it’s essential to address the limitations too. The cycle time can be longer compared to injection molding. Depending on the thickness of the walls, production can take several hours. That delay might not align with fast-paced market demands.
Moreover, achieving uniform wall thickness can sometimes be tricky. Unsuitable designs may lead to wasted materials. Industry studies suggest that optimizing designs can reduce waste by up to 30%. This emphasizes the need for careful planning before diving into the mold-making process. Ultimately, while rotational molding offers unique benefits for large components, it's crucial to navigate its challenges wisely.
| Molding Technique | Best For | Material Options | Typical Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotational Molding | Large, Hollow Parts | Polyethylene, Nylon, PVC | Storage Tanks, Playground Equipment, Toys | Low tooling costs, Uniform wall thickness | Long cycle times, Limited precision |
| Injection Molding | Small to Medium Parts | ABS, Polycarbonate, Polypropylene | Automotive Parts, Consumer Goods | High precision, Fast production | High initial cost, Complex setup |
| Blow Molding | Hollow Items | PET, HDPE | Bottles, Containers | Fast production, Cost-effective for high volumes | Limited shapes, Material limitations |
| Thermoforming | Shallow, Simple Shapes | PVC, PETG, Polystyrene | Packaging, Appliances | Lower tooling costs, Quick turnaround | Weaker parts, Limited design complexity |
Thermoforming is a key plastic molding technique favored for its speed and cost-effectiveness. This method excels in producing thin-walled components. The process involves heating plastic sheets until they become pliable. Once ready, these sheets are formed over a mold. Air pressure or vacuum helps create the desired shape. This technique is widely used in packaging, automotive, and medical industries.
However, there are challenges to consider. Thermoformed parts often lack the strength of injection-molded components. They may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads. Quality control can be an issue, as variations in sheet thickness affect the final product. Manufacturers must continuously refine their processes. Not every application suits thermoforming due to these limitations.
Despite its drawbacks, thermoforming remains popular. It offers a quick turnaround time for prototypes. It’s a great choice for businesses looking to scale production without hefty investments. Companies can experiment with designs and materials easily. This flexibility can lead to innovation. While it has imperfections, the benefits often outweigh the challenges.
This chart illustrates the cost efficiency of different plastic molding techniques, highlighting that thermoforming provides a quick and cost-effective solution for producing thin-walled components.





You are using an outdated browser. Things may not appear as intended. We recommend updating your browser to the latest version.
Close