In the ever-evolving landscape of modern manufacturing, the significance of stamped metal parts cannot be overstated. These components play a critical role across a multitude of industries, from automotive to aerospace, offering unmatched precision and efficiency. As technology advances, the demand for high-quality stamped metal parts is on the rise, with applications that extend well beyond conventional uses. By understanding the versatility of these components, manufacturers can harness their benefits to enhance product functionality and reduce production costs.
This guide delves into the various applications and advantages of stamped metal parts, providing insights into their essential role in the manufacturing process. Whether it's through intricate designs or robust structures, stamped metal parts offer a unique solution to meet the diverse needs of industry stakeholders. By examining the innovative techniques used in production and the various shapes and sizes these parts can take, we will explore how they contribute to improved efficiency and performance in several applications. Prepare to uncover the ultimate advantages that stamped metal parts bring to the manufacturing table.
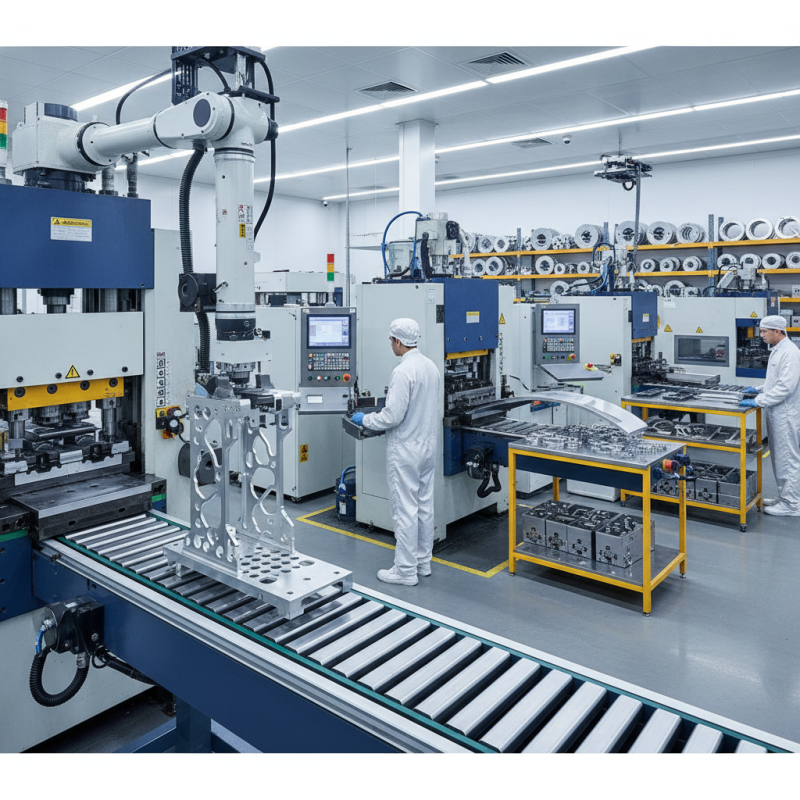

Stamped metal parts are integral components widely used across various industries due to their efficiency, precision, and versatility. The production process of stamped metal parts begins with the selection of raw materials, typically sheets of metal like steel, aluminum, or copper. These sheets are then fed into a stamping press, where they undergo a series of operations such as cutting, bending, and forming. The stamping process can be performed in different ways, including progressive stamping, which allows for multiple parts to be fabricated in a single run, enhancing productivity and reducing waste.
Once the stamping process is complete, the parts can be further treated through processes like deburring, painting, or coating, depending on their intended application. Stamped metal parts can be found in a multitude of products, from automotive components to consumer electronics and industrial machinery. Their production is characterized by high levels of repeatability and accuracy, making them ideal for mass production. The ability to create complex shapes and intricate designs also contributes to their widespread use, enabling manufacturers to produce lightweight yet strong components essential for modern technology.
This chart illustrates the various applications of stamped metal parts across different industries. The automotive sector leads with 40% usage, followed by aerospace at 25%, demonstrating the widespread reliance on stamped metal components in manufacturing processes.
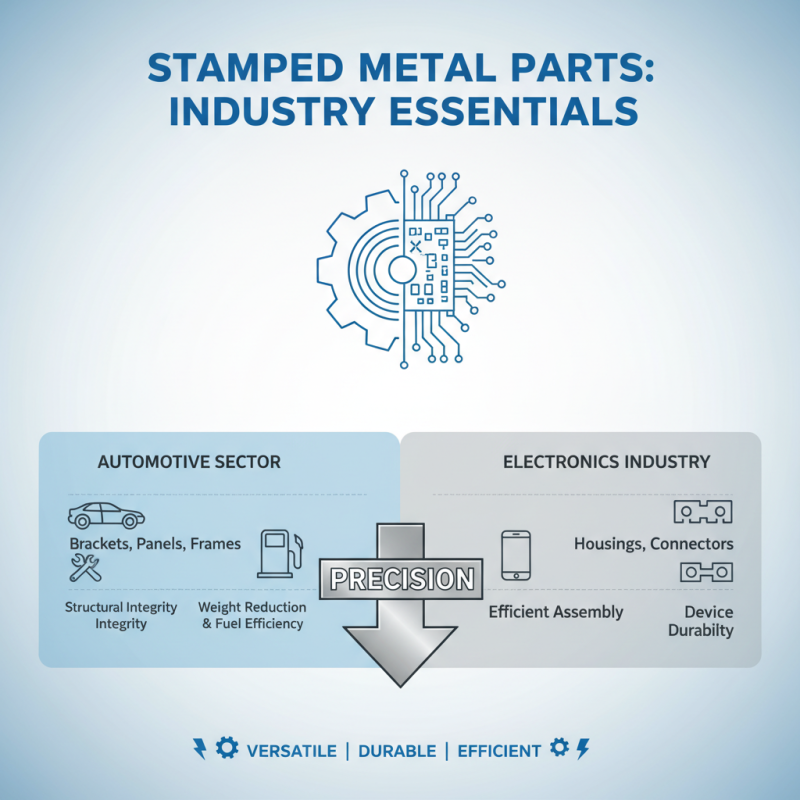
Stamped metal parts are essential components utilized across a myriad of industries, each benefiting from their unique properties and production methods. In the automotive sector, for instance, stamped metal parts are crucial for manufacturing precision components such as brackets, panels, and frames. These components not only ensure structural integrity but also contribute to weight reduction and increased fuel efficiency. In the electronics industry, stamped parts are used for housings and connectors, enabling efficient assembly processes and enhancing device durability.
In the appliance industry, stamped metal parts play a significant role in creating robust structures for household machines, ensuring longevity and reliability. The healthcare sector also relies on stamped metal components for medical devices, where precision and sterility are paramount.
Tips: When selecting stamped metal parts for your projects, consider factors such as material type, thickness, and tolerances. Choosing the right specifications can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the finished product. Additionally, collaborating with experienced manufacturers can provide insights into optimizing designs for manufacturability, which can lead to cost savings and improved production efficiency.
Stamped metal parts have gained popularity due to their efficiency and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional manufacturing methods. One significant advantage is the high precision and consistency that stamping provides. Unlike conventional methods that may involve machining or manual assembling, stamping utilizes dies to create parts in large quantities with minimal variation. This not only enhances the quality of the parts produced but also significantly reduces waste materials, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
Tips for manufacturers considering stamped metal parts include investing in modern stamping technology to improve speed and accuracy. Additionally, collaborating closely with engineers during the design phase can help identify potential complications and streamline production processes. Adopting a just-in-time inventory system can also optimize the benefits of stamped parts by aligning production closely with demand.
Another benefit of stamped metal parts is their versatility across various industries, from automotive to electronics. They can be easily tailored to meet specific design requirements without incurring high costs related to tooling changes. Choosing stamped components can lead to faster turnaround times, allowing businesses to respond rapidly to market changes. It's important to evaluate your production needs to fully capitalize on the competitive advantages stamped metal parts offer.
When selecting materials for stamped metal parts, a variety of factors must be considered, including strength, ductility, cost, and the environmental conditions to which the parts will be exposed. Common materials like steel, aluminum, and copper each offer distinct advantages. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the global market for metal stamping is projected to grow by 6% annually through 2025, highlighting the increasing demand for versatile and durable materials in manufacturing processes. Steel is favored for its strength and ability to withstand high-stress applications, while aluminum is preferred for its lightweight properties and corrosion resistance.
Tips: When choosing a material for your stamped parts, consider the specific application and any regulatory requirements. For instance, if your parts require high corrosion resistance and lightweight features, aluminum alloys may be a suitable choice. If you are looking for optimal strength, high-carbon steels could be the best option, offering excellent tensile strength and wear resistance.
Another crucial aspect of material selection is the processing method. Materials can behave differently under various stamping conditions, which can impact their performance and durability. A study from the Precision Metalforming Association emphasizes the importance of evaluating the machinability and formability of materials used for stamping. Understanding the characteristics of your chosen material will ultimately contribute to the efficiency and quality of the final product, ensuring that it meets both performance and cost expectations.
Tips: Engage with your material suppliers and seek their expertise on new materials that can enhance your stamped components' performance. Staying informed on emerging trends and technologies can help you leverage the right materials for innovative applications in your industry.
The world of stamped metal parts is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing industry demands. One of the most significant trends shaping the future of stamped metal part technologies is the increasing integration of automation and robotics in manufacturing processes. Automated stamping systems are becoming more precise and efficient, allowing for higher production rates and reduced waste. This shift not only enhances output but also enables manufacturers to produce complex geometries and intricate designs that were previously challenging to achieve with traditional methods.
In addition to automation, the use of advanced materials and lightweight alloys is becoming more prevalent in stamped metal applications. As industries such as automotive and aerospace seek to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, the demand for lighter yet durable components is growing. Innovations in material science are paving the way for the development of new alloys that maintain strength while reducing weight. This trend is complemented by the incorporation of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled devices, which allow for real-time monitoring and data analysis during the stamping process. These innovations are set to redefine standards in quality, efficiency, and sustainability across various sectors that rely on stamped metal parts.




You are using an outdated browser. Things may not appear as intended. We recommend updating your browser to the latest version.
Close