Sheet metal fabrication is a crucial process in modern manufacturing, serving as the backbone for a wide array of applications across various industries. As John Smith, a leading expert in sheet metal fabrication, states, "The precision and versatility of sheet metal fabrication allow for innovative designs that meet the ever-evolving demands of our global market." This statement underscores the significance of sheet metal in delivering solutions that are not only functional but also adaptable to different environmental and aesthetic requirements.
At its core, sheet metal fabrication involves transforming flat sheets of metal into finished components through a series of techniques, including cutting, bending, and assembling. These processes are vital in producing parts for industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, and electronics. The ability to manipulate metal into intricate shapes and forms makes sheet metal fabrication an essential aspect of modern engineering.
As we delve deeper into the key processes and applications of sheet metal fabrication, we will explore how this craft not only enhances product design but also contributes to sustainability through efficient use of materials. From prototype development to mass production, understanding these methodologies allows for better decision-making in project management and product lifecycle optimization.
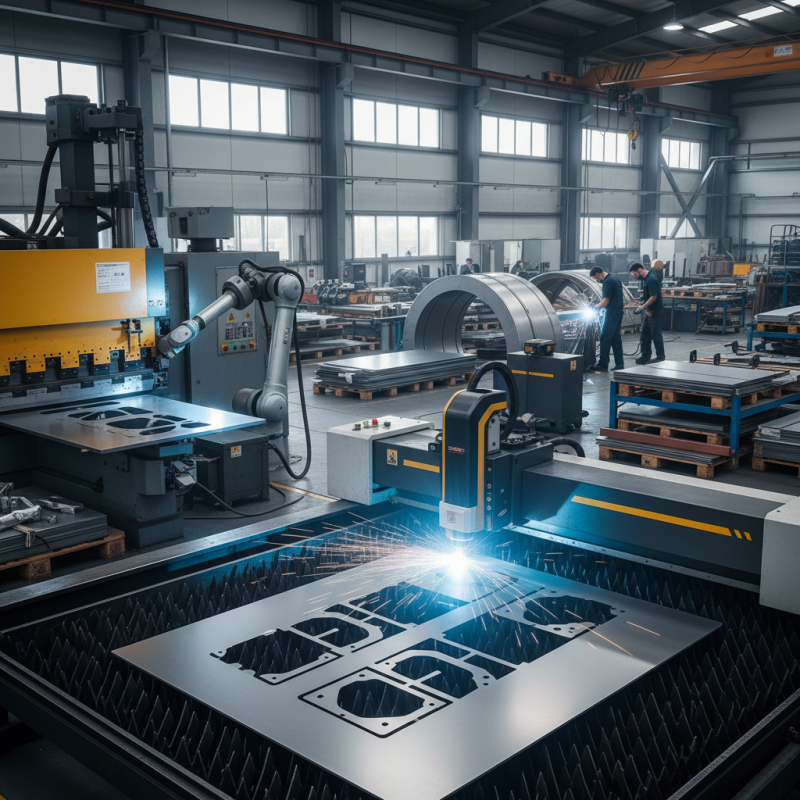

Sheet metal fabrication is a vital manufacturing process that involves transforming flat sheets of metal into a wide range of parts and structures. It encompasses various techniques such as cutting, bending, punching, and welding to achieve the desired shapes and dimensions. Each of these processes can be tailored to meet specific requirements, making sheet metal fabrication a versatile solution for different industries. The ability to manipulate metal sheets easily allows for the production of both simple and complex designs, ensuring the end products are functional and efficient.
In the world of manufacturing, sheet metal fabrication plays a crucial role in creating components for automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics, among others. The lightweight yet strong nature of metal makes it an ideal choice for applications where durability is essential. Furthermore, advancements in technology have led to the integration of automated processes and software that enhance precision and productivity. This evolution not only improves the overall quality of fabricated products but also reduces waste, thereby making the fabrication process more environmentally friendly.

Sheet metal fabrication encompasses a range of processes vital for shaping and assembling metal components used in various industries. Key processes in this field include cutting, bending, and assembling. Cutting is often performed using methods like laser cutting, shear cutting, or waterjet cutting, allowing for precise and intricate shapes to be produced from flat sheets of metal. Each technique has its unique advantages, making it suitable for different material types and thicknesses, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in the initial stages of fabrication.
Bending follows cutting and is essential in creating the desired angles and shapes of the metal pieces. This process can be achieved through press brakes or roll bending machines, which apply force to the metal sheet, enabling it to take on specific forms required for the final product. The accuracy of the bending process is crucial, as it directly influences the fit and function of the assembly in its intended application.
Lastly, assembling is a critical step that brings together various fabricated parts. Techniques such as welding, riveting, and adhesive bonding are commonly utilized to ensure durability and stability of the final product. Each of these methods provides unique characteristics that can enhance the overall integrity of the assembly, making them suitable for diverse applications such as automotive components, electronic enclosures, and structural steel frameworks. Understanding these key processes is essential for anyone involved in sheet metal fabrication, as they form the backbone of producing functional and precise metal products.
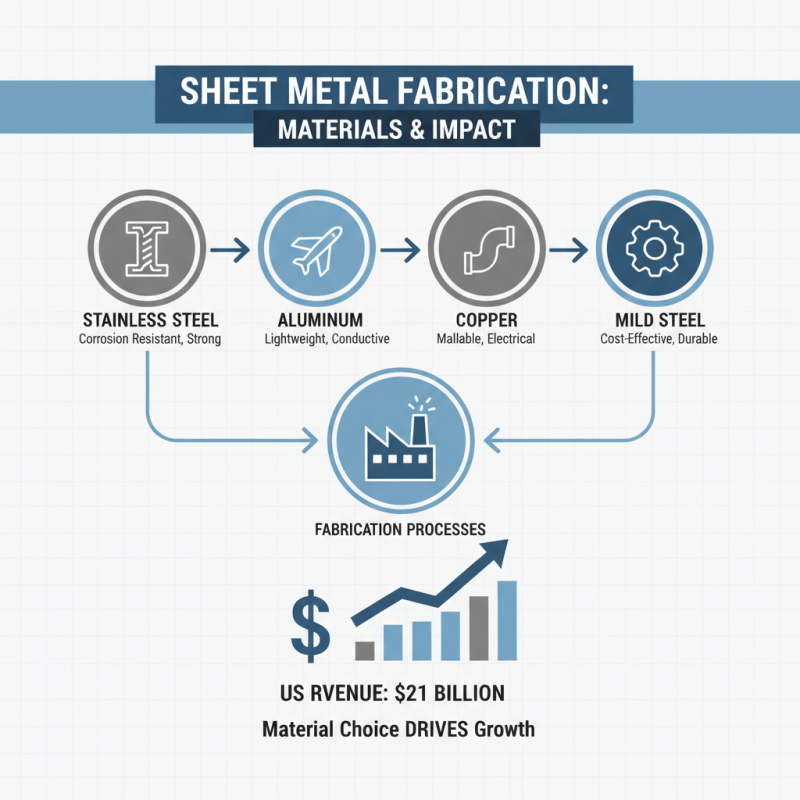
Sheet metal fabrication involves a range of processes to transform flat metal sheets into desired shapes and structures, and the choice of materials plays a crucial role in the effectiveness and efficiency of these operations. Commonly used materials in sheet metal fabrication include stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and mild steel, each offering unique benefits suited for specific applications. According to a report by IBISWorld, the sheet metal fabrication industry generated approximately $21 billion in revenue in the U.S., highlighting the significance of material selection in driving this growth.
Stainless steel, known for its corrosion resistance and durability, is widely employed in industries ranging from food processing to aerospace. In fact, the global market for stainless steel is projected to reach $160 billion by 2025, driven by its applications in high-performance environments. Aluminum, on the other hand, is favored for its lightweight properties and excellent malleability, making it ideal for automotive and construction applications. As reported by Grand View Research, the global aluminum market size is expected to reach $189.96 billion by 2026, underscoring the metal’s pivotal role in modern fabrication processes.
Sheet metal fabrication is integral to numerous industries, playing a crucial role in manufacturing and production. The process encompasses several key techniques, such as cutting, bending, and assembling, which enable the creation of components used in various applications. According to a report by the Research and Markets Group, the global sheet metal fabrication market is projected to reach $20 billion by 2026, emphasizing the growing demand for this technology across sectors.
In the automotive industry, sheet metal fabrication is vital for producing body panels, chassis, and other essential parts. With automotive manufacturers increasingly focusing on lightweight designs to enhance fuel efficiency, the use of aluminum and high-strength steel has surged. The International Aluminum Institute forecasts a 20% increase in aluminum usage in car manufacturing over the next decade, driven by the need for sustainable and efficient transportation solutions.
Additionally, the construction sector heavily relies on sheet metal fabrication for structural components, roofing, and insulation. The World Steel Association reports that around 50 million tons of steel are used annually in construction projects, underscoring the significance of sheet metal in creating durable and cost-effective structures. The versatility and adaptability of sheet metal fabrication enable it to meet the diverse requirements of industries, reinforcing its position as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
| Process | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | A high precision cutting method using a focused laser beam. | Automotive parts, complex shapes for art and design. |
| Bending | Forming process that involves bending sheet metal to a specified angle. | Enclosures, brackets, frames. |
| Welding | Joining two or more pieces of metal through heat and/or pressure. | Structural components, machinery fabrication. |
| Stamping | A process that uses a die to cut and shape material. | Automobile body parts, home appliances. |
| Punching | Creating holes in sheet metal using a punch and die set. | Electronic enclosures, HVAC components. |
| Finishing | Processes applied to the surface of metal parts to enhance appearance or corrosion resistance. | Consumer electronics, decorative items. |
Sheet metal fabrication offers several advantages that make it a popular choice across various industries. One of the primary benefits is its versatility. This process can produce a wide range of components, from simple brackets to complex enclosures, catering to diverse applications in automotive, aerospace, and construction sectors. Additionally, sheet metal fabrication allows for precision and consistency, ensuring that each part meets strict specifications and quality standards. Furthermore, it often results in reduced material waste compared to other manufacturing processes, promoting cost-effectiveness and environmentally friendly practices.
However, sheet metal fabrication also presents certain challenges that must be navigated. One significant issue is the skill level required for effective fabrication. Skilled labor is essential for operating specialized machinery and ensuring high-quality outcomes, which can sometimes lead to increased labor costs and training requirements. Additionally, the process can be limited by the thickness and type of material used, as certain metals may present difficulties during bending, cutting, or welding. These challenges necessitate careful planning and expertise to maximize the benefits of sheet metal fabrication while minimizing potential drawbacks.
This bar chart illustrates the efficiency percentage of various key processes in sheet metal fabrication. Laser cutting displays the highest efficiency at 95%, while bending and welding have efficiencies of 85% and 80% respectively. Stamping and finishing, although slightly lower, maintain competitive efficiencies at 75% and 90%. Understanding these processes helps identify their advantages and potential challenges in sheet metal fabrication.




You are using an outdated browser. Things may not appear as intended. We recommend updating your browser to the latest version.
Close