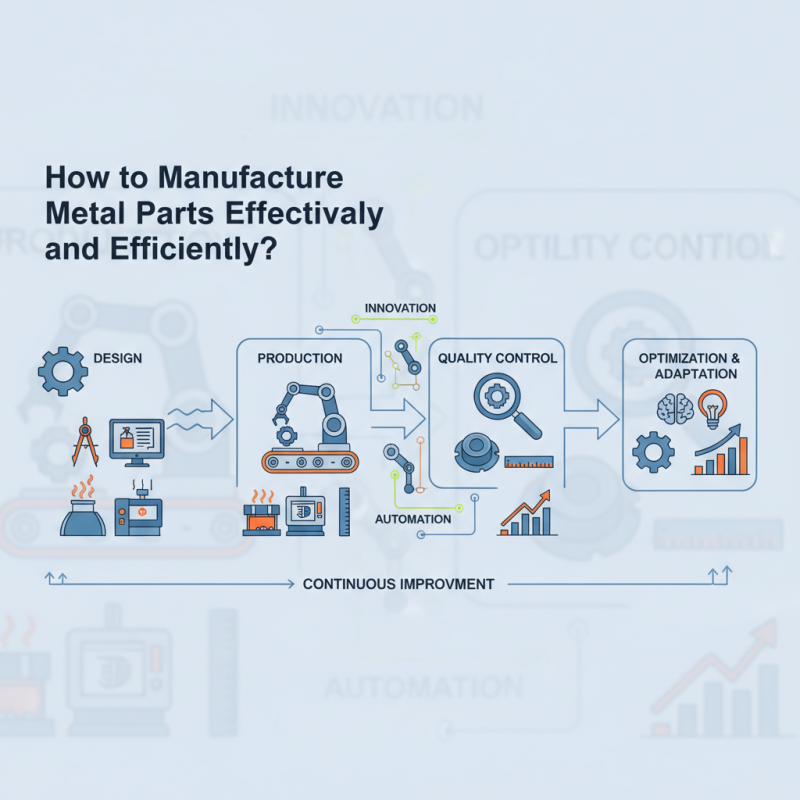
In the competitive realm of metal parts manufacturing, efficiency and effectiveness are paramount. According to Dr. James Anderson, an expert in the field, "Precision and speed are key in today's manufacturing landscape." His insight captures the essence of what is needed to thrive in this industry.
Metal parts manufacturing involves various processes, from design to production. Each step must be finely tuned to meet quality standards while minimizing waste. Companies often face challenges like outdated machinery or inefficient workflows. These issues can hinder productivity and lead to missed deadlines.
Innovative technologies and practices are crucial for overcoming these obstacles. Embracing automation, for example, can significantly streamline operations. Yet, many firms struggle with the transition, reflecting a need for adaptation. Continuous improvement is necessary to navigate this evolving landscape.
Manufacturing metal parts requires a firm grasp of various processes. Understanding material properties is crucial. For instance, steel, aluminum, and titanium each have unique characteristics. Choosing the right material affects durability and performance significantly.
A recent industry report indicates that around 30% of metal manufacturing processes lead to waste. This highlights inefficiencies that companies must address. Implementing lean manufacturing principles can help reduce waste. Automation also plays a role. It can improve production rates while maintaining quality. Yet, over-reliance on automation may hinder innovation and adaptability, which are vital in a rapidly changing market.
Additionally, skilled labor remains essential. Without trained workers, even the best equipment can underperform. Companies must invest in training programs to enhance skills. The human factor cannot be overlooked. Finding the right balance between technology and human expertise is a challenge that requires ongoing reflection and adjustment.
| Manufacturing Process | Advantages | Typical Materials | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | High precision, versatility | Aluminum, Steel, Titanium | Aerospace, Automotive, Medical |
| Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | Complex shapes, cost-effective for mass production | Stainless Steel, Copper, Alloys | Consumer Electronics, Medical Devices |
| Die Casting | High production speed, smooth surface finish | Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium | Automotive Parts, Gearboxes |
| Laser Cutting | Precision cutting, minimal material waste | Steel, Brass, Carbon Steel | Signage, Metal Art, Industrial Parts |
| Forging | Strong mechanical properties, high durability | Steel, Aluminum, Copper Alloys | Heavy Machinery, Aerospace Components |
Effective metal fabrication processes rely on a variety of techniques. Understanding these methods enhances production efficiency and product quality. One effective technique is precision cutting. Using advanced cutting tools ensures accuracy. This minimizes material waste and optimizes the design.
Tips: Always evaluate your cutting tools. Ensure they are sharp and well-maintained. Dull tools create rough edges and can lead to errors.
Welding is another vital technique. Proper welding techniques ensure strong seams. Different materials require specific welding methods. Yet, improper technique can lead to weak joints. Regular training and skill assessment can prevent such issues.
Tips: Inspect your welds frequently. Small flaws can become major problems. A simple visual check can save time in the long run.
Finally, finishing processes like polishing and coating enhance durability. They protect parts and improve appearance. However, overlooking the finishing stage may lead to rust or wear.
Tips: Allocate time for finishing. Rushing through this stage can compromise quality. Quality parts start with thorough finishing.
In today’s manufacturing landscape, efficiency is key. Advanced technologies play a vital role in optimizing production processes for metal parts. Integrating automation can dramatically reduce costs. Machines can run continuously, leading to faster output. Real-time monitoring systems track progress and identify inefficiencies quickly. However, relying solely on machines has its drawbacks. Human oversight is essential for quality control.
Additive manufacturing has gained popularity for its ability to create complex parts. This method reduces material waste and leads to lighter products. Yet, the technology is not foolproof. Issues like layer adhesion and print accuracy require constant evaluation. Workers must adapt to new skills, which can be a hurdle for some.
Implementing AI in production can optimize workflows. Algorithms analyze data to predict machinery failures and maintenance needs. However, integrating AI can be daunting. Training staff while keeping production steady poses a challenge. Balancing innovation with traditional techniques requires careful planning. The path to efficiency is paved with both advancements and learning opportunities.
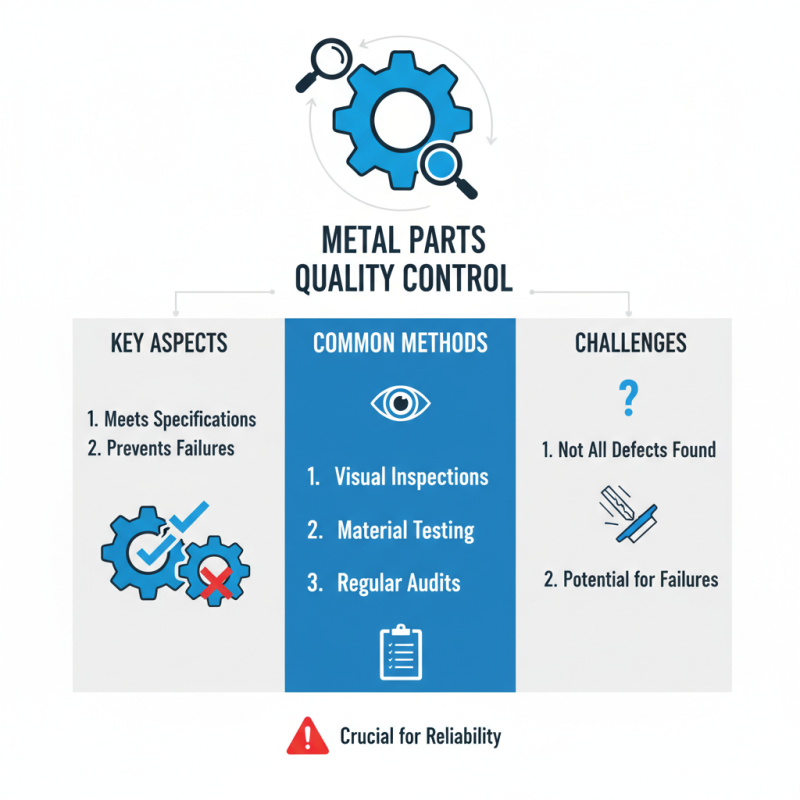
Quality control is crucial in metal parts production. It ensures that every part meets the required specifications. Common methods include inspections and testing. Regular audits help identify issues early. However, not all inspections catch every problem. Some defects slip through, leading to potential failures later.
Another important aspect is the use of advanced technologies. Automated machines can enhance accuracy but may overlook subtle flaws. Human oversight is still necessary. Training workers to spot inconsistencies can be beneficial. They bring a keen eye that machines might miss. Continuous feedback loops help in refining processes.
Tracking metrics is essential for improvement. Monitoring production rates and defect rates provides insight. If defects rise, immediate action is needed. Adjusting processes based on data can guide production. Yet, reliance on metrics can create complacency. A balance between data and hands-on checks is critical.
Sustainable practices in the metal manufacturing industry are essential for reducing environmental impact. The process of metal production often involves high energy consumption and waste generation. Implementing energy-efficient technologies is one way to mitigate this. For instance, using renewable energy sources can significantly lower carbon footprints.
Additionally, recycling metal scrap can lead to substantial resource savings. Many manufacturers still discard scrap material, losing potential revenue. It’s crucial to rethink this approach. Instead of throwing away waste, they should consider investing in recycling technologies that convert scrap back into usable materials.
Training employees on sustainability practices is another key area. Often, workers are unaware of the importance of their actions. Simple changes, like minimizing waste or optimizing machinery use, can make a real difference. However, companies must consistently evaluate and improve these practices. Embracing sustainability in metal manufacturing requires commitment and ongoing reflection on existing methods.





You are using an outdated browser. Things may not appear as intended. We recommend updating your browser to the latest version.
Close