High pressure die casting is a sophisticated manufacturing process that enables the production of complex metal components with exceptional precision and efficiency. This method utilizes high pressure to inject molten metal into a mold, allowing for faster production cycles while maintaining rigorous tolerances. As industries increasingly seek ways to enhance productivity and reduce waste, high pressure die casting has emerged as a key player, providing significant advantages in terms of material utilization and surface finish.
The benefits of high pressure die casting extend beyond mere cost savings; they encompass improved mechanical properties and consistent quality across mass-produced items. This technique is particularly advantageous for creating parts with intricate geometries, which are often challenging to achieve through traditional methods. As manufacturers continue to innovate and optimize their processes, understanding the high pressure die casting process becomes essential for those looking to leverage its potential for increased efficiency and competitive edge in the market.

High pressure die casting (HPDC) is a manufacturing process that involves forcing molten metal at high pressure into a mold to produce precise and complex parts. This technique is commonly used with non-ferrous metals, primarily aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys, due to their favorable properties and lightweight characteristics. According to industry reports, the HPDC market is expected to grow significantly, reaching an estimated value of over $10 billion by 2026, driven by the rising demand for lightweight materials in automotive and aerospace applications.
The key advantages of high pressure die casting include enhanced production efficiency and superior surface finish. This method allows for rapid cycle times, often producing products in mere seconds. Additionally, components produced via HPDC have higher dimensional accuracy and reduced post-processing requirements, particularly crucial for industries that demand high tolerance levels.
A study from the Allied Market Research highlighted that the process reduces material waste by approximately 20%, making it not only cost-effective but also more environmentally friendly compared to traditional casting methods. As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability, the benefits of HPDC in reducing waste and energy consumption become more critical in the manufacturing landscape.
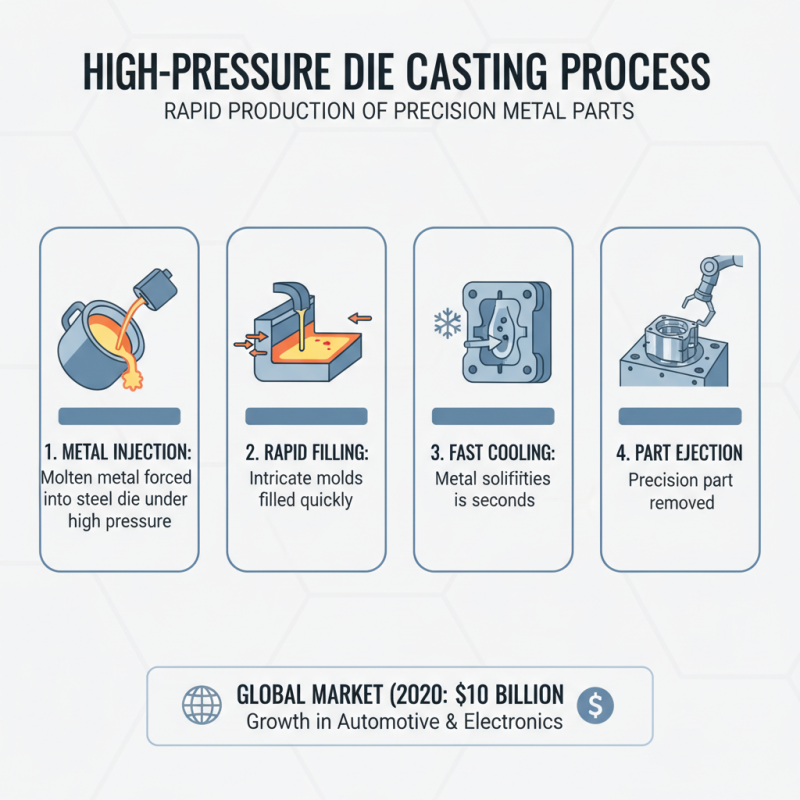
The high pressure die casting process is a sophisticated manufacturing technique that allows for the rapid production of metal parts with precision and consistency. This process can be broken down into key steps that highlight its efficiency and effectiveness. Initially, molten metal is injected into a steel die under high pressure, which helps in filling intricate molds quickly. The quick cooling of the metal solidifies the product faster than traditional casting methods, usually within a few seconds. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global die casting market was valued at approximately $10 billion in 2020, with expectations of significant growth driven by innovations in the automotive and electronics industries.
Once the metal has cooled and solidified, the die is opened, and the part is ejected. This step is critical as it minimizes cycle times, enabling manufacturers to produce large quantities of high-quality parts in a short period. The overall process not only enhances productivity but also reduces waste, as excess metal can be reused. Furthermore, the extremely high-pressure conditions ensure that the final product possesses strong mechanical properties and precise dimensions. A study by Freedonia Group indicates that the demand for die-cast products is anticipated to grow at a rate of 5.7% annually through 2025, underscoring the ongoing relevance of this method in modern manufacturing.
High pressure die casting (HPDC) is a widely utilized manufacturing process known for its efficiency and precision in producing complex metal components. A variety of materials can be employed in this process, with aluminum and zinc alloys being the most popular choices due to their favorable characteristics. Aluminum alloys offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. According to a report by the Research and Markets, the global aluminum die casting market is expected to grow significantly, projected to reach USD 10.5 billion by 2025, demonstrating the increasing reliance on this material in high-pressure applications.
When considering materials for HPDC, it’s crucial to understand the specific requirements of your project. For instance, magnesium is another material gaining traction in the industry due to its lightweight properties, especially in automotive components. Additionally, copper alloys, while less common, are utilized for their thermal conductivity and toughness in specialized applications. Selecting the right material not only influences the production cost but also affects the final product's performance and longevity.
**Tips:** Ensure proper alloy selection by consulting with material specialists early in the design phase. Conducting thorough material compatibility tests can save time and costs during production. Additionally, consider the environmental impact of your material choices; options like recycled aluminum can be both cost-effective and sustainable.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process Description | A manufacturing process where molten metal is injected into a mold at high pressure to create parts. |
| Common Materials | Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium, Copper alloys |
| Key Benefits | High dimensional accuracy, smooth surface finish, complex geometries, reduced waste, and fast production rates. |
| Applications | Automotive parts, aerospace components, electronic housings, and consumer products. |
| Environmental Impact | More efficient metal usage reduces waste and energy consumption compared to traditional casting methods. |
High pressure die casting is a widely utilized manufacturing process known for its efficiency and precision in producing metal components. One of its most significant benefits is the ability to create complex geometries with high dimensional accuracy. This is particularly advantageous in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where the performance and reliability of components are crucial. The high-speed injection of molten metal into a mold facilitates rapid production cycles, which helps reduce lead times and improve overall productivity.
In addition to speed and accuracy, high pressure die casting offers excellent material utilization and reduced waste. The process allows for thinner walls in cast parts, resulting in lighter components without compromising strength. This is especially beneficial in sectors aiming for energy efficiency and weight reduction, such as automotive manufacturing. Furthermore, the smooth surface finish obtained from the casting process often eliminates the need for extensive machining, lowering production costs even further. By leveraging these advantages, manufacturers can enhance product quality while maintaining competitive pricing in the market.
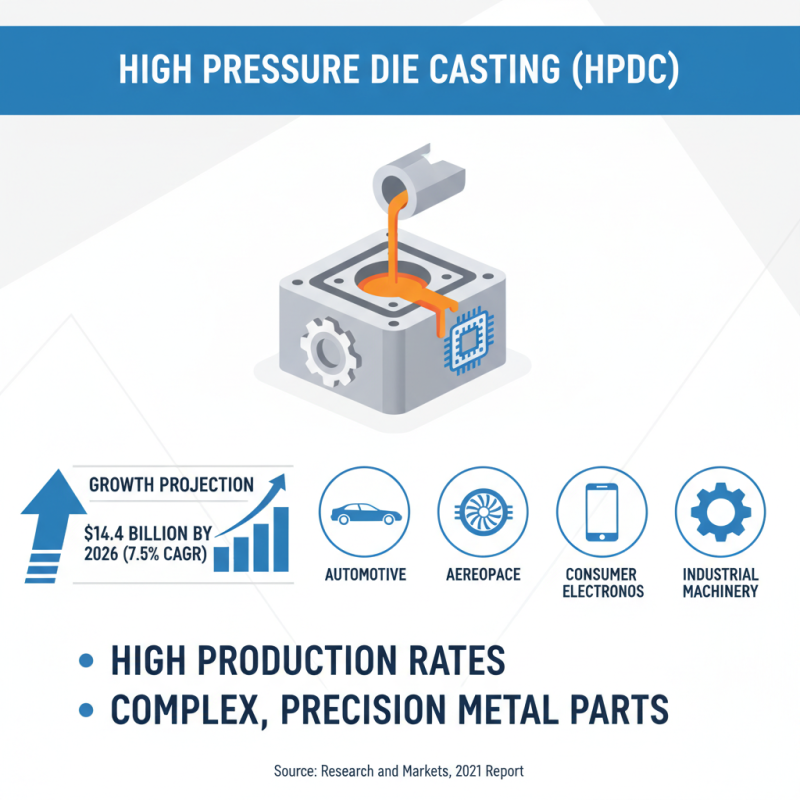
High pressure die casting (HPDC) is increasingly favored in industries that require high production rates and the ability to produce complex metal parts with precision. This technology is widely utilized in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, and industrial machinery. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global die casting market, which includes high pressure die casting, is projected to reach approximately $14.4 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of about 7.5% from 2021. This growth underscores the versatility and efficiency of HPDC in meeting the demands of modern manufacturing.
In the automotive industry, HPDC is particularly prominent for producing lightweight components that contribute to fuel efficiency and performance. Engine blocks, transmission cases, and other critical parts are frequently manufactured using this method due to its ability to create components with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. A study by the Die Casting Association indicates that utilizing HPDC can reduce the weight of components by up to 30% compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Similarly, in consumer electronics, components such as housings and brackets are made with HPDC, allowing for intricate designs while maintaining robust durability and reducing overall manufacturing costs. The ability to recycle aluminum and zinc alloys used in HPDC further enhances its appeal across various sectors, emphasizing sustainability alongside efficiency.






You are using an outdated browser. Things may not appear as intended. We recommend updating your browser to the latest version.
Close