Mastering sheet metal work techniques is a vital skill for artisans and fabricators alike. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a novice looking to enhance your skills, understanding the fundamental principles of working with sheet metal is essential. This craft not only requires a keen eye for detail but also a solid grasp of the various tools and methods that can transform raw metal into functional and aesthetically pleasing forms.
In this guide, we will explore the top ten essential tips to elevate your sheet metal work techniques to the next level. From selecting the right materials to mastering cutting and joining methods, each tip is designed to provide practical advice and insights that you can apply to your projects. Moreover, we will emphasize the importance of safety and precision throughout the process, ensuring that you achieve high-quality results with each piece you create. Whether you are crafting custom parts, artistic designs, or practical components, these tips will help you refine your skills and improve your outcomes in the fascinating world of sheet metal work.
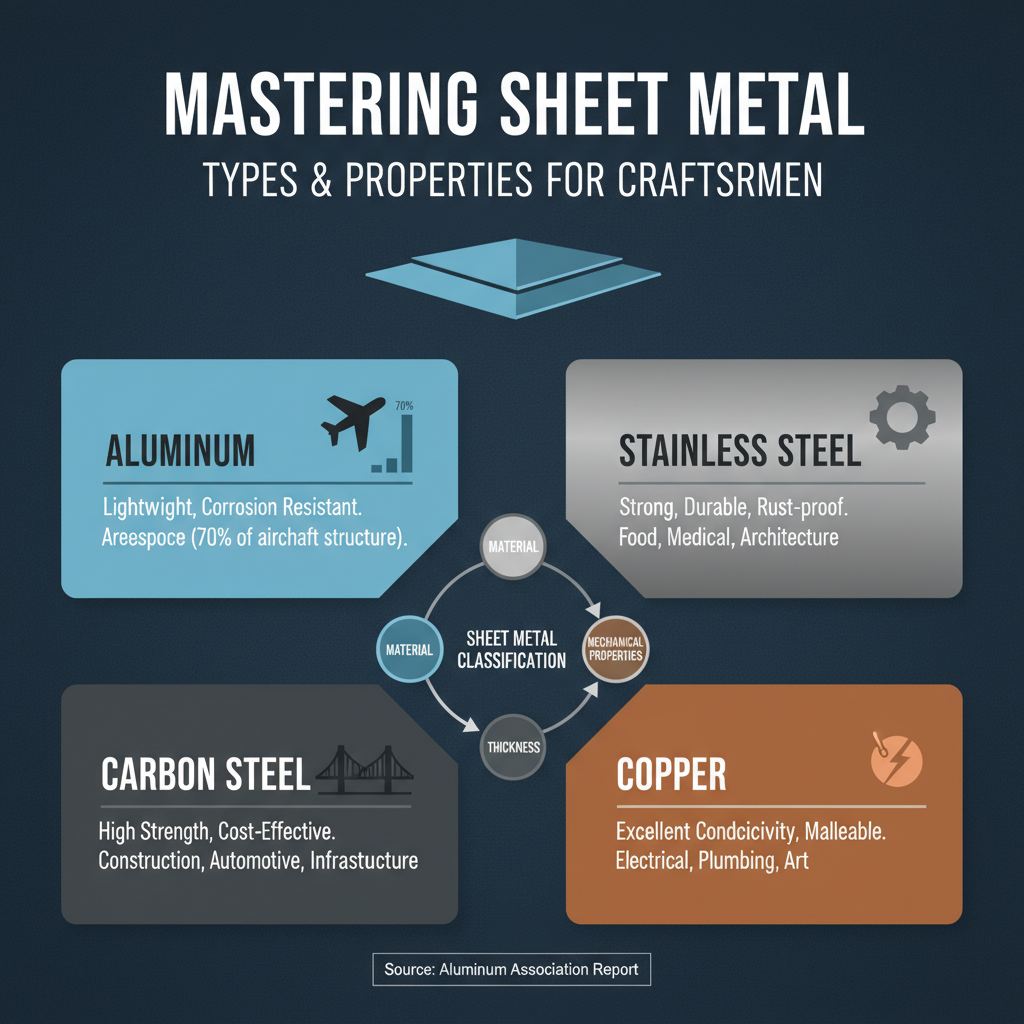
Understanding the properties and types of sheet metal is crucial for anyone looking to master sheet metal work techniques.
Sheet metal is classified based on its material composition, thickness, and mechanical properties.
Common types include aluminum, stainless steel,
carbon steel, and copper, each offering distinct advantages and challenges.
For instance, aluminum is prized for its lightweight and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in the aerospace industry,
where a report by the Aluminum Association highlights that it accounts for nearly 70% of the structural weight of modern aircraft.
The mechanical properties of sheet metal, such as tensile strength and ductility, determine how well it can be formed and manipulated.
According to a study by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), materials with higher tensile strength typically require specialized cutting tools and techniques
to prevent deformation during processing. Understanding these properties allows craftsmen to select the appropriate metal
for their projects, enabling efficient fabrication while reducing waste and costs. With growing advancements in metalworking technologies, such as
CNC machining and laser cutting,
staying informed about material performance ensures that artisans can produce high-quality products that meet rigorous industrial standards.
When diving into the art of sheet metal work, having the right tools and equipment is paramount to achieving precision and efficiency. According to a recent industry report by Freedonia Group, the market for sheet metal fabrication tools is projected to reach $6.3 billion by 2025, indicating a growing demand for high-quality equipment. Essential tools for sheet metal work include shears, which are used to cut metal sheets with speed and accuracy, and metal brakes that allow for bending sheets into various shapes.
Investing in high-quality, specialty tools is critical, as they can significantly enhance both the quality of work and productivity.
Furthermore, safety equipment cannot be overlooked. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) emphasizes that proper safety gear, including gloves, protective eyewear, and respiratory masks, reduces the risk of accidents in metalworking environments by up to 60%. Having a well-equipped workshop not only boosts efficiency but also adheres to safety standards that protect workers. With the right tools and an emphasis on safety, beginners and seasoned professionals alike can master the techniques of sheet metal work effectively.
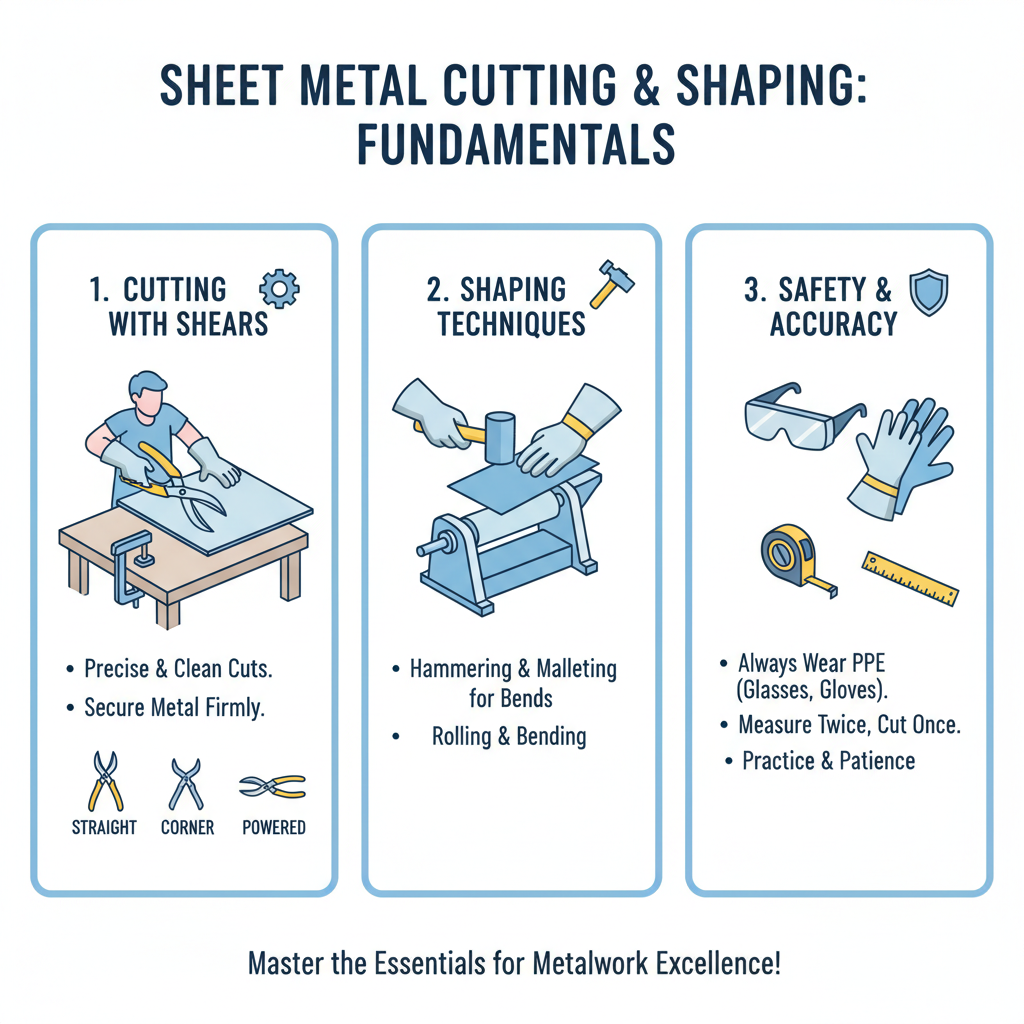
Mastering the fundamental techniques for cutting and shaping sheet metal is essential for anyone looking to excel in metalwork. One of the primary methods for cutting sheet metal is the use of shears, which allow for precise and clean cuts. Different types of shears, such as straight, corner, and even powered shears, provide versatility for various projects. When using shears, it is important to secure the sheet metal firmly to prevent any movement during the cutting process, ensuring accuracy and safety.
Shaping sheet metal often involves techniques such as bending and forming, which can be accomplished using tools like a brake or a hammer. A brake allows for uniform bends, creating angles that are both strong and aesthetically pleasing. On the other hand, hammers can be used for more intricate shaping, enabling the craftsman to create curves and other detailed forms. Combining these techniques with proper measurements and layout will lead to precise results, enhancing the overall quality of the finished product.
Practicing these fundamental skills not only improves proficiency but also boosts confidence in tackling more complex metalworking projects.
When it comes to mastering sheet metal work, knowing the best practices for joining and fastening sheet metal parts is crucial for achieving strong and durable assemblies. One essential tip is to always ensure that the edges of the metal sheets are clean and free from contaminants before joining them. This helps create a better bond, whether you are welding or using adhesives. Additionally, aligning the parts accurately before fastening can significantly enhance the integrity of the connection.
Another key practice involves selecting the appropriate fastening method based on the application. For instance, using rivets can provide a reliable and robust connection for various sheet metal structures, while self-tapping screws can be ideal for quicker assembly without the need for pre-drilled holes. It's also important to consider the thickness of the metal and the load requirements, as this will influence the choice of fastener and technique.
Lastly, leveraging clamps during the fastening process can help maintain the alignment of the sheets while securing them. Using clamps not only ensures a tight fit but also minimizes the risk of warping or distortion during welding or fastening. By incorporating these tips into your sheet metal work practices, you’ll achieve better results and extend the lifespan of your projects.
When working with sheet metal, safety should always be the top priority. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), workplace injuries are significantly reduced when proper safety protocols are followed. In industries involving metal fabrication, the injury rate can range from 3 to 5 incidents per 100 workers annually, highlighting the importance of risk management in sheet metal work environments.
To minimize hazards, workers should always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, safety goggles, and steel-toed boots. It's essential to ensure that tools and machinery are well-maintained and that safety guards are in place. Additionally, training programs should be implemented to educate employees about safe handling techniques and emergency procedures. According to a recent report from the National Safety Council, companies that invest in comprehensive safety training can see a 40% reduction in incidents. Adhering to these guidelines not only fosters a safer working environment but also enhances productivity and morale on the shop floor.
| Tip Number | Technique | Safety Guidelines | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Proper PPE | Always wear safety glasses and gloves. | Using personal protective equipment reduces the risk of injury from sharp edges and flying debris. |
| 2 | Tool Safety Checks | Inspect tools before use. | Ensure that tools are in good working condition to prevent malfunctions and accidents. |
| 3 | Secure Workpieces | Use clamps to secure metal sheets. | Stable workpieces prevent slips and injuries while cutting or bending. |
| 4 | Ventilation | Ensure proper ventilation in the workspace. | Good airflow minimizes health risks from fumes produced during cutting or welding. |
| 5 | Fire Safety | Keep fire extinguishers accessible. | Preparedness for fires is crucial when working with flammable materials. |
| 6 | Ergonomic Posture | Maintain proper posture while working. | Correct posture helps prevent musculoskeletal disorders. |
| 7 | Cutting Techniques | Use appropriate cutting methods for materials. | Different materials require different techniques to ensure safety and precision. |
| 8 | Safe Disposal | Dispose of scrap metal safely. | Eliminates hazards from leftover material that could cause injuries. |
| 9 | Electrical Safety | Follow electrical safety protocols. | Prevent electric shock when using power tools. |
| 10 | Training and Certification | Invest in proper training for all workers. | Ensures that all personnel are knowledgeable about safety and techniques. |
You are using an outdated browser. Things may not appear as intended. We recommend updating your browser to the latest version.
Close